
In the digital age, the realm of commerce is increasingly intertwined with the virtual world, presenting both opportunities and challenges. This section delves into the critical strategies necessary to fortify the electronic defenses of nascent organizations. It explores how to shield sensitive information from potential digital incursions, ensuring the continuity and integrity of operations.
Understanding the Landscape: As technology evolves, so do the methods of those who seek to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems. For startups and small enterprises, the stakes are particularly high. A single breach can have devastating consequences, affecting not only the financial stability but also the reputation of the business.
Building Resilience: This article outlines practical steps that can be taken to enhance the robustness of your digital infrastructure. From implementing robust authentication protocols to regularly updating software, each measure plays a crucial role in creating a secure environment for your business operations.
Understanding Cybersecurity Basics
In this section, we delve into the fundamental knowledge necessary to recognize and mitigate digital risks. Recognizing the various forms of digital threats is crucial for maintaining a secure environment, especially for entities operating in the digital realm.
Identifying Common Cyber Threats
Cyber threats come in many forms, each posing unique risks to the integrity and confidentiality of data. Here, we explore some of the most prevalent types:
- Malware: This term encompasses a variety of malicious software, including viruses, worms, and ransomware. Malware typically infiltrates systems through deceptive downloads or links, often leading to data corruption or theft.
- Phishing: Phishing involves fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. It is a common tactic used to deceive users into providing access to critical systems or information.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: These attacks occur when a perpetrator secretly intercepts and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. Common examples include eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic.
- SQL Injection: This type of attack involves inserting malicious SQL queries into input fields for execution. The goal is to manipulate backend databases to access information that was not intended to be displayed, including private user details.
Understanding these threats is the first step towards implementing effective defense mechanisms. Each threat requires specific countermeasures, which we will explore in subsequent sections of this article.
Identifying Common Cyber Threats
In this section, we delve into the identification of prevalent digital risks that organizations often face. Understanding these threats is crucial for maintaining a robust defense against potential breaches.
Malware is a broad term that encompasses various types of malicious software, including viruses, worms, and ransomware. These programs are designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system.
Phishing attacks are another common threat, where attackers use fraudulent emails or messages to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information or downloading harmful software.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks occur when a cybercriminal intercepts communication between two parties. This type of attack can lead to the theft of data or unauthorized access to systems.
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks aim to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with traffic.
Lastly, insider threats involve risks posed by individuals within an organization, whether intentional or accidental. These threats can result from misuse of access privileges or negligence.
By recognizing these common digital threats, organizations can better prepare and implement strategies to mitigate risks and protect their assets.
Implementing Strong Password Policies

In the realm of digital defense, establishing robust password protocols is paramount. This section delves into the strategies and best practices to fortify access controls, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure against unauthorized entry.
The Importance of Strong Passwords
Passwords serve as the first line of defense against intruders. A weak password can be easily cracked, providing unauthorized individuals with access to critical data. Therefore, it is essential to enforce the creation of complex passwords that are difficult to guess or decipher through automated means.
Guidelines for Password Complexity
To enhance security, passwords should include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. The length should also be sufficient, typically recommended to be at least eight characters long. Encouraging the use of passphrases, which are longer and more memorable, can also significantly increase security.
Regular Password Changes
Implementing a policy that requires regular updates to passwords can mitigate the risk of them being compromised over time. However, it is crucial to balance this with user convenience to avoid the creation of weaker passwords due to frequent changes.
Education and Compliance
Ensuring that all users understand the importance of these policies and how to comply with them is vital. Regular training sessions and reminders can help reinforce the need for strong, unique passwords and the avoidance of common pitfalls such as using personal information or common words.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can significantly enhance their digital defenses, making it much more challenging for potential attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication
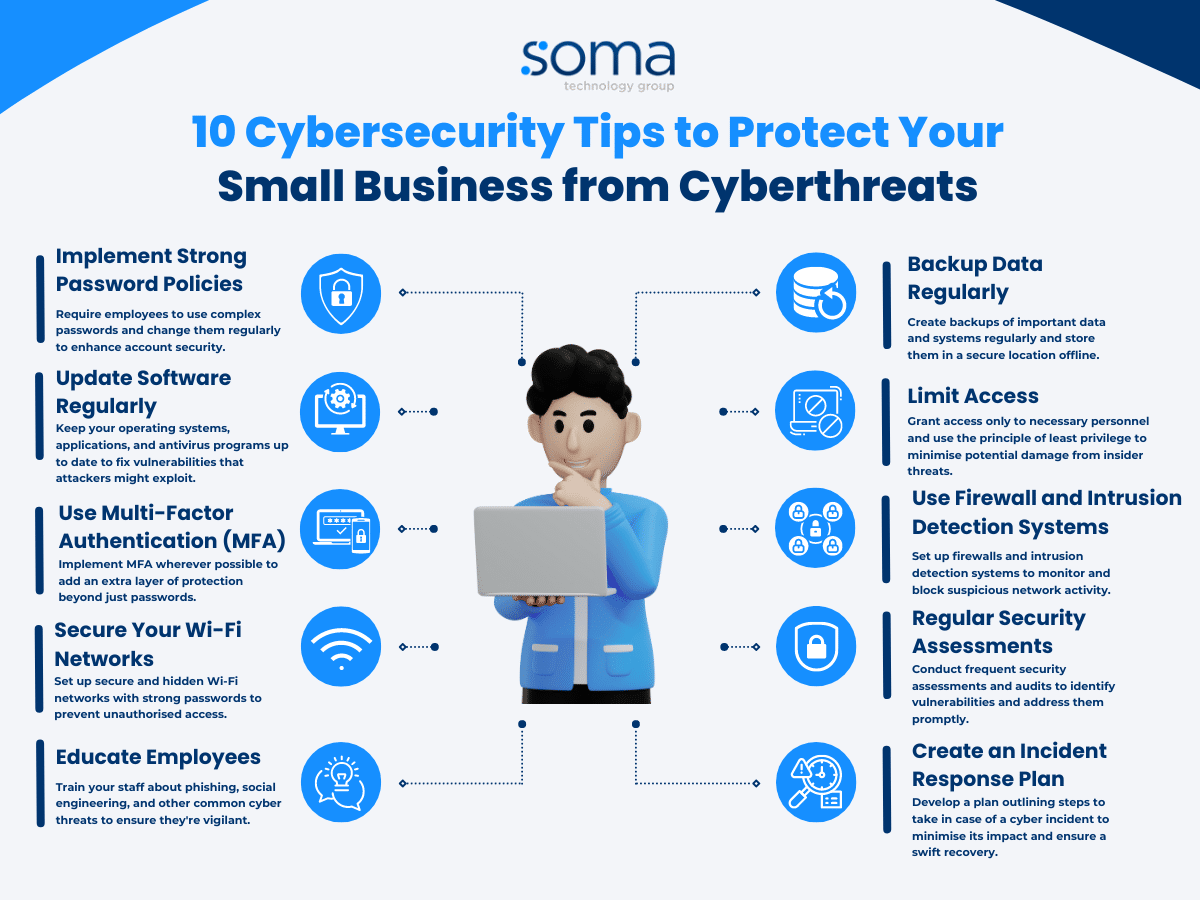
In the realm of digital defense, enhancing the security of access points is paramount. This section delves into the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA), a critical strategy that significantly fortifies the integrity of user logins. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA acts as a robust barrier against unauthorized entry, safeguarding sensitive information and systems.
Multi-factor authentication operates on the principle of combining at least two different components: something you know (like a password), something you have (such as a smart card or mobile device), and something you are (biometrics). This layered approach makes it substantially more difficult for potential intruders to gain access, even if they manage to decipher one of the factors.
- Password and PIN: The first layer often involves traditional passwords or personal identification numbers (PINs), which must be kept confidential and complex to deter brute force attacks.
- Physical Tokens: These are tangible devices that generate a unique code, which must be entered in addition to a password. Examples include key fobs or USB tokens.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones can be used to receive one-time codes via SMS or through authentication apps, adding an extra layer of security.
- Biometrics: This includes fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, providing a highly personalized and secure method of verification.
Implementing MFA requires careful planning and consideration of the specific needs and resources of the organization. It is essential to integrate MFA into the broader security framework, ensuring compatibility with existing systems and protocols.
- Assessment of Needs: Evaluate which systems and data require the highest level of protection and prioritize their integration with MFA.
- Employee Training: Educate staff on the importance of MFA and how to use it properly to avoid security lapses.
- Regular Updates: Keep MFA systems updated to address any vulnerabilities and to ensure continued effectiveness against emerging threats.
In conclusion, multi-factor authentication is a powerful tool in the arsenal of digital defense. By adding layers of verification, it significantly enhances the security of user accounts and critical systems, making it a vital component in the comprehensive strategy of protecting digital assets.
Securing Your Network Infrastructure
In this section, we delve into the critical strategies to fortify the digital framework of an organization. Ensuring the integrity and security of a network is paramount to safeguarding against unauthorized access and potential breaches. This involves a comprehensive approach to network protection, which includes both preventive measures and active monitoring.
One of the most prevalent and insidious threats to network security is phishing. Phishing attacks are designed to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords and financial details, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in digital communications. These attacks can be incredibly sophisticated, often involving detailed social engineering tactics to manipulate victims.
To combat phishing, it is essential to implement robust training programs for all staff members. This training should cover the identification of phishing attempts, understanding the typical signs of such attacks, such as suspicious email addresses or unexpected attachments, and the correct procedures to report and handle such incidents. Regular updates and drills can help keep employees vigilant and prepared.
Additionally, technological safeguards play a crucial role in defending against phishing. This includes the use of advanced email filters that can detect and quarantine phishing emails before they reach the user’s inbox. Implementing strict access controls and regularly auditing user permissions can also help minimize the risk of successful phishing attacks.
Lastly, fostering a culture of security awareness within the organization is vital. Encouraging employees to question and verify the legitimacy of any unexpected or suspicious communications can significantly reduce the vulnerability of the network to phishing attacks. By combining these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their defenses against this pervasive threat.
Protecting Against Phishing Attacks
In this section, we delve into the critical strategies to shield against deceptive attempts aimed at extracting sensitive information. Phishing, a prevalent tactic, involves tricking individuals into revealing confidential details through seemingly legitimate communications. Understanding and implementing effective countermeasures is essential to fortify your digital defenses.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
The first step in protection is awareness. Phishing emails often mimic reputable sources, featuring familiar logos and language. However, they may contain subtle discrepancies such as misspelled domain names or unusual requests for personal data. Always scrutinize the sender’s email address and the content for inconsistencies.
Educating Staff
Employee education plays a pivotal role in mitigating phishing risks. Regular training sessions should cover how to identify suspicious emails, the importance of verifying the authenticity of requests, and the correct protocol for reporting potential phishing attempts. Encourage a culture of vigilance and open communication regarding potential threats.
Using Technology to Combat Phishing
Deploying advanced email filters and security software can significantly reduce the likelihood of phishing emails reaching your inbox. These tools are designed to detect and block messages that match known phishing patterns. Regular updates to these systems ensure they remain effective against emerging phishing techniques.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding an extra layer of security through 2FA can thwart phishing attempts. Even if an attacker manages to obtain login credentials, the additional verification step, such as a code sent to a mobile device, acts as a robust barrier. Encourage the use of 2FA across all sensitive accounts.
Regularly Updating Security Protocols
As phishing methods evolve, so should your security protocols. Regular reviews and updates to your security policies ensure they remain effective against new threats. This proactive approach helps maintain a strong defense against phishing and other cyber threats.
By integrating these strategies, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience against phishing attacks, safeguarding valuable data and maintaining operational integrity.
Managing and Updating Software Regularly

In the realm of digital operations, ensuring that all software is up-to-date and well-managed is crucial. This section delves into the importance of regular updates and effective management practices to safeguard against vulnerabilities and maintain operational integrity.
Regular updates to software are not just a matter of keeping up with the latest features; they are essential for security. Updates often include patches for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious entities. Here are several strategies to ensure your software remains secure and efficient:
- Automated Updates: Utilize software that automatically updates itself. This ensures that you are always running the latest version without manual intervention.
- Scheduled Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of all software to check for updates. This practice helps in identifying and installing updates that might not be automated.
- Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management system. This involves tracking, evaluating, and installing patches promptly to minimize exposure to threats.
- Security Audits: Regularly perform security audits to identify any outdated software that might pose a risk. These audits can help prioritize updates based on the level of risk associated with each piece of software.
- User Education: Educate all users about the importance of not disabling automatic updates and reporting any issues or outdated software immediately.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can significantly enhance their defense against potential digital threats and ensure that their operational software remains robust and secure.
Educating Employees on Cybersecurity

In the realm of digital defense, ensuring that all team members are well-informed is crucial. This section delves into the strategies and practices necessary to equip employees with the knowledge and skills to safeguard against digital vulnerabilities. By fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience to various forms of electronic threats.
To effectively educate employees, it is essential to cover a range of topics that are pertinent to their daily interactions with digital tools and networks. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Understanding Basic Threats: Employees should be familiar with common digital threats such as malware, ransomware, and phishing attempts. Providing clear examples and scenarios can help them recognize and avoid these threats.
- Password Management: Teaching best practices for creating strong, unique passwords and the importance of changing them regularly can prevent unauthorized access.
- Safe Browsing Habits: Instructing on how to safely navigate the internet, including recognizing suspicious links and emails, can reduce the risk of falling victim to attacks.
- Data Handling: Educating on the proper handling of sensitive information, both in digital and physical forms, is crucial. This includes understanding the importance of encryption and secure file transfer methods.
- Incident Reporting: Establishing clear protocols for reporting suspicious activities or breaches can help in timely response and mitigation of potential damage.
Regular training sessions and updates are vital to keep the knowledge of employees current with the evolving landscape of digital threats. Incorporating interactive elements such as quizzes, role-playing scenarios, and real-world examples can enhance engagement and retention of information.
Furthermore, fostering a culture where questions and concerns about digital safety are encouraged can lead to a Read more on Medium vigilant and proactive workforce. By investing in the education of employees, organizations not only protect their digital assets but also empower their teams to be part of the solution in the ongoing battle against digital threats.
Backing Up Data Effectively
Ensuring the safety and accessibility of critical information is paramount in today’s digital landscape. This section delves into the strategies and tools necessary to effectively safeguard your data against unforeseen events, providing peace of mind and operational continuity.
Choosing the appropriate tools for data backup involves careful consideration of various factors, including the nature of the data, the frequency of updates, and the recovery time objectives. Here are some key considerations to guide your selection:
- Type of Data: Different types of data require different backup solutions. For instance, databases might need continuous backup solutions, while static files could be backed up less frequently.
- Frequency of Updates: Data that changes frequently will necessitate more regular backups to ensure all updates are captured.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This metric dictates how quickly data must be restored after a loss event. Depending on your operational needs, you might require real-time backup solutions or less frequent but more comprehensive backups.
When selecting a backup tool, it’s essential to evaluate the following features:
- Ease of Use: The tool should be user-friendly, allowing for easy setup and management of backups.
- Scalability: As your data grows, the backup solution should be able to scale accordingly without significant additional costs or complexity.
- Security: Ensure the tool encrypts data both in transit and at rest to protect against unauthorized access.
- Reliability: The tool should have a proven track record of successful data recovery in various scenarios.
- Support and Updates: Regular updates and responsive customer support are crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of the backup solution over time.
In conclusion, selecting the right backup tools is a critical component of a comprehensive data protection strategy. By considering the specific needs of your data and operations, you can choose a solution that ensures the integrity and availability of your information when it matters most.
Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Tools
In this section, we delve into the critical task of selecting appropriate defense mechanisms to safeguard digital assets. The right tools can significantly enhance the resilience of an organization against various digital threats. It is essential to understand the landscape of available options and how they can be tailored to fit specific needs.
When evaluating potential defense mechanisms, consider the specific vulnerabilities and risks that your organization faces. Different tools offer varying levels of protection against malware, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other digital hazards. For instance, intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities, while encryption tools protect data integrity and confidentiality.
It is also crucial to assess the compatibility of these tools with your existing infrastructure. Integration issues can lead to inefficiencies and gaps in protection. Additionally, consider the scalability of the tools; as your organization grows, your defense mechanisms should be able to adapt and provide continued protection.
User-friendliness is another key factor. Tools that are complex to manage can lead to human errors, which are often the weakest link in digital defense. Training staff to use these tools effectively should also be part of your evaluation process.
Lastly, do not overlook the importance of regular updates and support from the tool providers. The digital threat landscape is constantly evolving, and tools must be updated to address new vulnerabilities and threats. Reliable customer support can be invaluable when dealing with complex issues or when rapid response is needed.
In conclusion, selecting the right defense mechanisms involves a careful balance of understanding your organization’s specific needs, evaluating tool capabilities, and ensuring compatibility and ease of use. By making informed decisions, you can significantly bolster your organization’s resilience against digital threats.
Monitoring and Responding to Cyber Incidents
In this section, we delve into the critical processes of surveillance and reaction to digital breaches. It is essential for organizations to not only detect but also effectively manage any unauthorized digital incursions. This involves a proactive approach to monitoring activities within the digital environment and a swift, informed response to any anomalies detected.
Effective surveillance of digital operations is the first line of defense against unauthorized access. This involves the use of sophisticated tools that can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs in real-time. By setting up alerts for suspicious activities, organizations can quickly identify potential threats and take necessary actions to mitigate risks.
Responding to a digital breach requires a well-defined strategy. This includes isolating affected systems to prevent further damage, conducting a thorough investigation to understand the scope and nature of the breach, and implementing corrective measures. It is crucial to have a team in place that is trained and ready to handle such incidents, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
Moreover, post-incident analysis is vital. It helps in understanding the weaknesses that led to the breach and in strengthening the overall defense mechanisms. Regular updates to response protocols and continuous training of staff are also part of an effective response strategy.
In conclusion, monitoring and responding to digital incidents are integral parts of safeguarding an organization’s digital assets. By maintaining vigilant surveillance and having a robust response plan, organizations can significantly reduce the impact of any digital security breach.